
Given, Emf of cell, E1 = 1.25 V
Balance point is obtained at, l1 = 35 cm
When, the cell is replaced by another cell
New balance point is, l2 = 63 cm
Emf of the second cell can be found out using the relation,
Now, substituting values we get,
Given,
Number density of electrons, n = 8.5 x 1028 m–3 Current carried by the wire, I = 3.0 A
Area of cross-section of the wire, A = 2.0 x 10–6 m2
Length of the wire, l = 3.0 m
Charge on electron, e = 1.6 x 10–19 C
Using the formula for Drift velocity
Therefore,
Time taken by an electron to drift from one end to another end is,
Given,
Surface charge density of earth's surface = 10–9 C/m2
Current flowing across the surface of earth, I = 1800 A
The radius of earth,r= 6370 km = 6.37 x 106 m
Charge on entire surface of the earth, q=
Area of earth's surface, A = 4
This implies,
q=4 (6.37 x 106)2 x 10–9 C
Using the formula , I= we get,
t=
Therefore,
Time required for the flow of entire charge is,

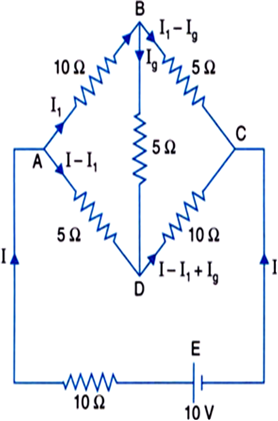
Given,
Emf of secondary cells,
Internal resistance of cell, r= 0.015
Number of secondary cells, n=6
External resistance, R = 8.5
Current drawn from the supply, I =
And, terminal voltage of the supply is, V=IR
